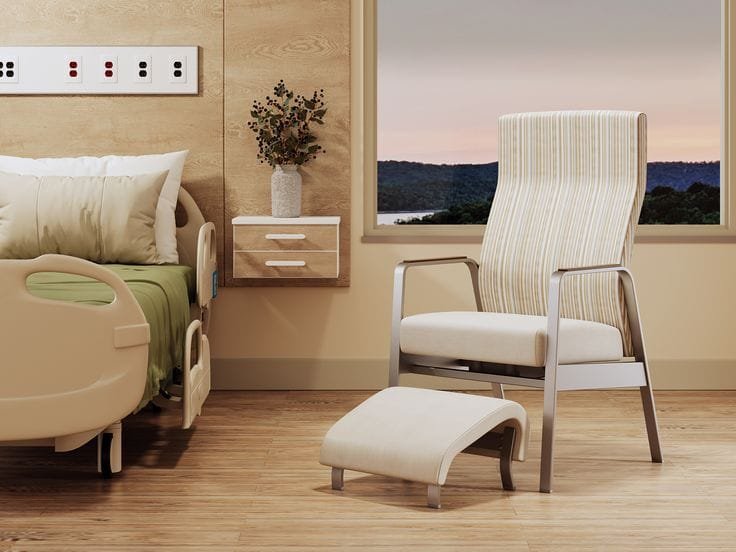

Have you ever considered how standard hospital furniture fundamentally fails patients with obesity, creating not only physical discomfort but also psychological distress and potential safety hazards? Healthcare facilities failing to provide appropriately-sized bariatric furniture deny obese patients dignity, compromise clinical outcomes, and expose facilities to significant liability risks. Research demonstrates that patients with obesity experience increased hospital anxiety, reluctance to seek healthcare, and worse medical outcomes when facilities lack appropriate accommodation. Yet many hospitals continue treating bariatric furniture as a specialty niche rather than a standard care requirement, despite obesity affecting over 40% of American adults and rising globally. Understanding bariatric furniture specifications, capacity ratings, safety considerations, and clinical implications enables healthcare administrators, designers, and clinical staff to create truly inclusive medical environments supporting safe, dignified care for all patients regardless of body size.
Introduction
Bariatric hospital furniture represents far more than oversized standard equipment—it embodies a commitment to inclusive, dignified healthcare meeting the evolving needs of diverse patient populations. Proper bariatric furniture specification affects patient safety, caregiver safety, clinical outcomes, and institutional liability while communicating organizational values regarding patient dignity and inclusive care. Modern healthcare design recognizes that appropriately-sized, weight-capacity-rated furniture represents a clinical standard rather than an optional accommodation, essential to meeting ethical care obligations and increasingly required by healthcare accreditation standards.
In this comprehensive guide, you will discover:
- Bariatric furniture specifications and capacity standards enabling proper equipment selection
- Size and weight capacity ranges across major furniture categories and their clinical applications
- Safety considerations affecting patient outcomes, caregiver injury prevention, and institutional liability
- Furniture selection and procurement strategies ensuring appropriateness for patient populations
- Dignity and inclusion principles guiding bariatric care space design
By understanding comprehensive bariatric furniture requirements, healthcare facilities can create truly inclusive environments supporting safe, dignified care for patients across all body sizes while protecting both patient and caregiver safety.
Understanding Bariatric Furniture Categories and Specifications
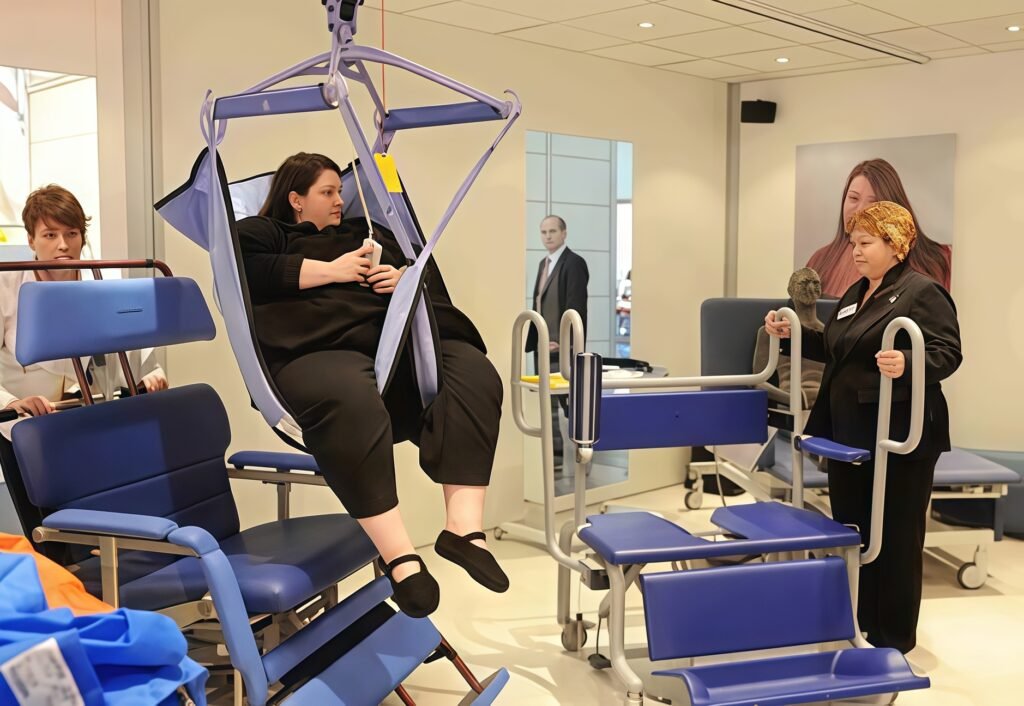
Defining Bariatric Furniture and Clinical Applications
Bariatric hospital furniture encompasses specialized equipment designed to safely support patients weighing 300+ pounds, with options extending to 600+ pounds and beyond for super-obese populations. Bariatric specifications represent engineering modifications to standard equipment addressing structural integrity, weight distribution, safety features, and operational functionality for higher-capacity applications.
Fundamental bariatric design differences:
Structural modifications:
- Reinforced frames using heavier-gauge steel or additional support materials
- Wider bases distributing weight across larger floor area preventing tip-over
- Strengthened attachment points withstanding greater stress loads
- Enhanced mechanical systems accommodating increased weight without compromise
- Upgraded electrical components (for powered equipment) rated for higher loads
- Safety margins built into specifications exceeding actual expected use
Capacity rating standards:
Industry-standard capacity ratings:
- Standard hospital furniture: 250-300 pounds typical capacity
- Bariatric furniture: 400-600 pounds common range
- Heavy-duty bariatric: 600-1,000 pounds for super-obese populations
- Specialty/custom: 1,000+ pounds for exceptional cases
- Safety margins: Manufacturers typically design to 150-200% of rated capacity
Clinical applications requiring bariatric specifications:
Hospital environments:
- Patient beds for medical/surgical patient accommodation
- Examination and procedure tables for diagnostic testing and interventions
- Transfer equipment (stretchers, gurneys) for patient transport
- Toilet seats and commodes for bathroom facilities
- Chairs and recliners for patient sitting and recovery
- Imaging equipment tables for radiology and diagnostic procedures
- Surgical tables for operative procedures
Specialized care environments:
- Intensive care units requiring specialized monitoring equipment
- Emergency departments serving acute patient populations
- Operating rooms with specialized surgical requirements
- Rehabilitation units supporting patient mobility and recovery
- Long-term care facilities serving chronic bariatric populations
- Mental health facilities serving behavioral health populations
| Table 1: Bariatric Furniture Capacity Categories and Specifications |
| Furniture Category | Standard Capacity | Bariatric Capacity | Super-Bariatric Capacity | Weight Safety Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Beds | 250-300 lbs | 450-600 lbs | 600-850 lbs | 150-200% rated capacity |
| Patient Chairs | 250-350 lbs | 400-700 lbs | 500-900 lbs | 150-200% rated capacity |
| Exam Tables | 300-350 lbs | 500-700 lbs | 700-1,000 lbs | 150-200% rated capacity |
| Stretchers/Gurneys | 300-400 lbs | 500-800 lbs | 800-1,200 lbs | 150-200% rated capacity |
| Toilet Seats | 200-250 lbs | 400-600 lbs | 600-800 lbs | 150-200% rated capacity |
| Commodes | 250-300 lbs | 450-700 lbs | 600-900 lbs | 150-200% rated capacity |
Bariatric Beds and Transfer Equipment Specifications
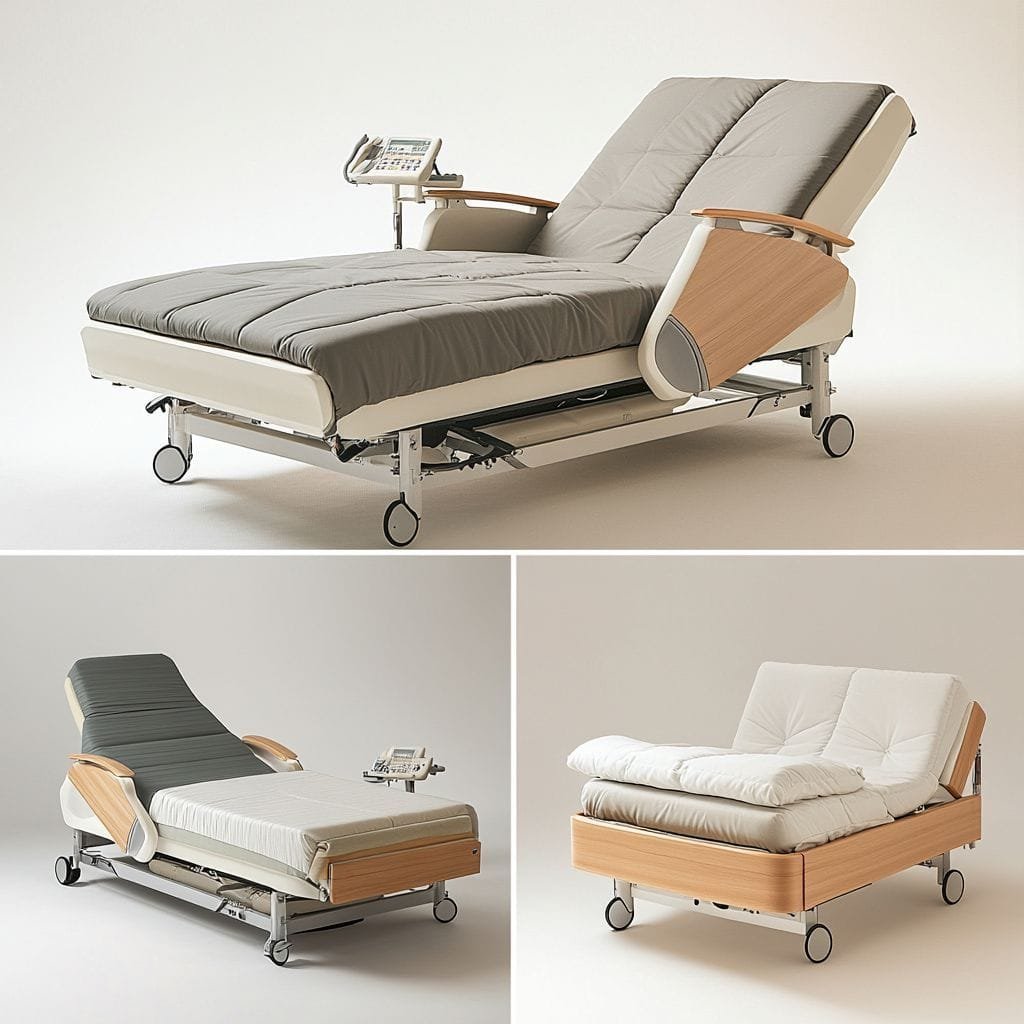
Hospital Bed Specifications and Weight-Bearing Requirements
Hospital beds represent the most critical bariatric furniture category, directly supporting patient safety during extended stays and frequent transfers.
Bariatric bed design specifications:
Structural and dimensional requirements:
- Reinforced frame construction using high-tensile steel or structural aluminum
- Width: 36-40 inches (vs. standard 30-36 inches) accommodating larger body widths
- Length: 80-84 inches standard (some extra-length options available)
- Height adjustability: 16-24 inch range enabling proper caregiver positioning and patient transfer
- Weight capacity: 450-600 pounds standard, up to 850+ pounds for specialty models
- Mattress platform: Reinforced to prevent sagging or failure under distributed load
- Electrical systems: Heavy-duty motors and controls rated for maximum-capacity operation
Safety features essential for bariatric applications:
- Bed rail systems structurally rated for bariatric patients requiring support during transfers
- Brake systems with enhanced locking preventing bed movement during patient transfer
- Emergency backup power enabling height adjustment during electrical failure
- Smooth, quiet operation reducing patient anxiety during positioning
- Easy-access control panels enabling patient self-positioning when appropriate
- Integrated scale options enabling weight monitoring without patient transfer
Mechanical considerations:
- Motor power and specifications ensuring smooth, reliable operation under maximum load
- Bearing and hinge systems rated for continuous heavy-use operation
- Hydraulic or pneumatic systems providing consistent operation without fatigue or drift
- Maintenance protocols preventing accelerated wear from maximum-capacity use
- Replacement parts availability ensuring long-term serviceability
Mattress specifications for bariatric patients:
Pressure ulcer prevention and comfort:
- Extra-firm support preventing excessive sagging under distributed weight
- Minimum 5-6 inch thickness providing adequate pressure distribution
- Memory foam or air-surface options optimizing pressure relief
- Waterproof, cleanable covers enabling hygiene management and incontinence accommodation
- Flame-retardant materials meeting hospital safety standards
- Specialized covers for patients with high pressure ulcer risk
Transfer Equipment and Mobility Support
Safe patient transfer represents a critical bariatric care consideration affecting both patient and caregiver safety.
Stretchers and gurneys for bariatric transport:
Weight-capacity specifications:
- Bariatric stretchers: 500-800 pound capacity standard
- Super-bariatric models: 800-1,200+ pound capacity for heaviest patients
- Reinforced frame construction ensuring structural integrity during transport
- Smooth-rolling casters with adequate braking systems
- Secure restraint systems preventing patient movement during transport
- Comfortable padding reducing pressure during extended transport
Specialized features:
- Stable, wide base preventing tip-over during transfers
- Height adjustability accommodating varied caregiver heights and transfer methods
- Split-frame construction enabling easier passage through narrow doorways
- Manual and powered options supporting different facility capabilities
- Integrated scales enabling weight monitoring during transport
Patient lifting equipment for bariatric care:
Critical safety infrastructure:
- Ceiling-mounted lift systems rated for bariatric patients (typically 500-700 lbs)
- Portable hydraulic lifts for rooms lacking permanent installation
- Wide slings appropriately sized for larger bodies
- Motorized assistance reducing caregiver back strain and injury risk
- Regular maintenance and inspection ensuring safety and reliability
- Staff training protocols ensuring proper use and safety
| Table 2: Transfer Equipment Specifications and Safety |
| Equipment Type | Standard Capacity | Bariatric Capacity | Super-Bariatric | Key Safety Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Stretcher | 300-400 lbs | 500-800 lbs | 800-1,200 lbs | Stable base, smooth transport, secure restraints |
| Patient Lift | 300-400 lbs | 500-700 lbs | 600-900 lbs | Motorized, durable slings, rated capacity |
| Ceiling Lift System | 300-400 lbs | 500-700 lbs | 600-900 lbs | Fixed installation, reliability, backup systems |
| Portable Lift | 250-350 lbs | 400-600 lbs | 600-800 lbs | Mobility, easy operation, maintenance |
| Transfer Bench | 250-350 lbs | 450-700 lbs | 600-900 lbs | Secure positioning, comfort, stability |
Examination, Procedure, and Bathroom Facilities
Bariatric Examination and Procedure Tables
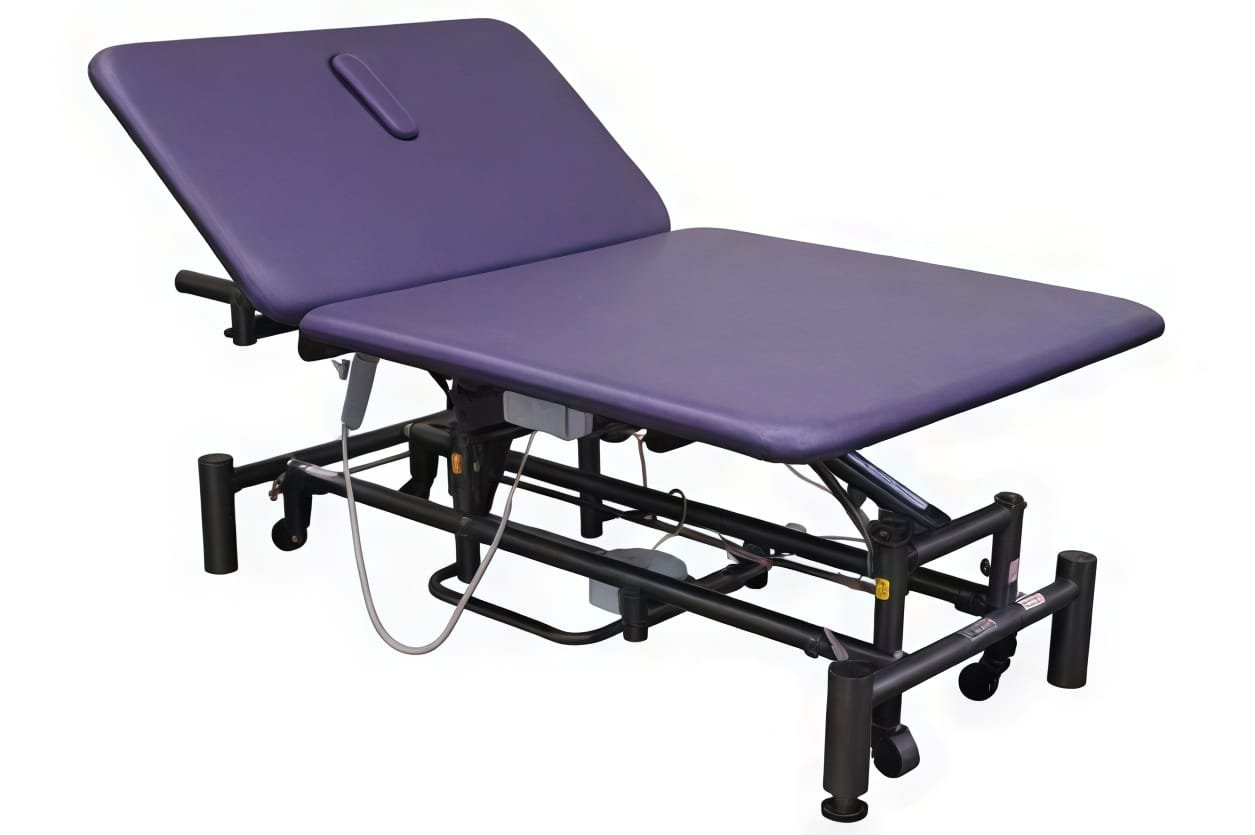
Specialized examination facilities require equipment supporting safe, dignified clinical assessment and intervention.
Exam table specifications for bariatric patients:
Dimensional and weight-capacity requirements:
- Width: 28-32 inches standard vs. 36-40 inches for bariatric models
- Weight capacity: 500-700 pounds standard bariatric; 700-1,000 pounds super-bariatric
- Adjustable height: 18-30 inch range enabling ergonomic physician positioning
- Adjustable back and leg support accommodating patient comfort positioning
- Reinforced construction supporting frequent positioning changes
- Easy-clean surfaces compatible with infection control protocols
Specialized features supporting bariatric examinations:
- Wider, more durable cushioning providing comfort and pressure relief
- Stable footrests supporting patient safety and comfort
- Accessible step stools (if exam table height requires assistance)
- Quiet, smooth mechanisms reducing patient anxiety
- Permanent or semi-permanent installation ensuring stability
- Privacy considerations (screens, curtains) supporting dignity
Diagnostic and imaging equipment for bariatric patients:
Radiology and imaging table considerations:
- Weight capacity ensuring safe imaging of bariatric patients
- Wide, comfortable surfaces accommodating larger body dimensions
- Stable, reliable mechanics enabling precise imaging positioning
- Radiation shielding considerations maintaining standard protection protocols
- Image quality capabilities enabling diagnostic-quality imaging of heavier patients
- Extended intervals between maintenance due to heavier use
Bariatric Bathroom and Toilet Facilities
Bathroom facilities represent a critical dignity and safety concern for bariatric patients in hospital settings.
Toilet seat and commode specifications:
Weight-capacity and dimensional requirements:
- Bariatric toilet seats: 400-600 pound capacity standard
- Super-bariatric seats: 600-900 pound capacity for heaviest patients
- Seat width: 17-18 inches standard vs. 20-24 inches for bariatric models
- Reinforced seat frame preventing collapse or failure
- Elevated height options (17-19 inches) reducing strain during transfers
Safety and comfort features:
- Secure, non-slip surfaces preventing sliding during use
- Substantial armrests (if applicable) supporting transfer assistance
- Splash guards preventing spills and contamination
- Easy-clean, antimicrobial surfaces supporting hygiene protocols
- Removable seats enabling easier cleaning and maintenance
- Locking mechanisms preventing unwanted movement
Bathroom grab bars and safety infrastructure:
Essential accessibility features:
- Reinforced grab bars rated for weight-bearing (rated 500+ lbs typical)
- Appropriate positioning supporting safe transfers and stability
- Firm mounting into structural supports (never drywall alone)
- Multiple grab bar options accommodating varied patient heights and needs
- Non-slip, secure handholds preventing slipping during use
- Regular inspection ensuring structural integrity
Bathing and showering facilities:
Bariatric shower and bathing considerations:
- Roll-in shower capability accommodating wheelchair or stretcher access
- Shower chairs rated for bariatric use (500-700 lbs typical)
- Non-slip flooring and grab bars preventing falls
- Accessible controls enabling patient or caregiver operation
- Adequate space (36-48 inches minimum) accommodating caregiver assistance
- Waterproof, mold-resistant construction maintaining hygiene
| Table 3: Bariatric Bathroom and Toilet Facility Specifications |
| Facility Type | Standard Capacity | Bariatric Capacity | Super-Bariatric | Key Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toilet Seat | 250-300 lbs | 400-600 lbs | 600-900 lbs | Width 17-18″ vs 20-24″, height options |
| Commode | 250-350 lbs | 450-700 lbs | 600-900 lbs | Mobile option, splash guard, easy-clean |
| Shower Chair | 300-400 lbs | 500-700 lbs | 700-900 lbs | Waterproof, non-slip, caregiver access |
| Grab Bars | 300-400 lbs | 500-700 lbs | 600-900 lbs | Reinforced, properly mounted, multiple options |
Safety Considerations and Caregiver Protection
Patient Safety and Clinical Outcomes
Proper bariatric furniture directly impacts patient safety, clinical outcomes, and healthcare equity.
Patient safety implications of inadequate bariatric furniture:
Physical safety risks:
- Equipment failure or collapse causing falls, injuries, or mortality
- Fall hazards from inappropriate seat heights or unstable surfaces
- Skin breakdown from inadequate pressure relief on insufficient cushioning
- Limited mobility when equipment doesn’t support transfer or movement
- Procedural complications when patients cannot be properly positioned for examination or treatment
- Medication errors resulting from inability to assess or treat patients properly
Psychological and dignity impacts:
- Humiliation and shame from being visibly squeezed into standard-sized furniture
- Healthcare avoidance reducing likelihood of future care seeking
- Increased anxiety and stress during vulnerable medical encounters
- Reduced treatment compliance when patients distrust facility commitment to care
- Depression and emotional distress from disrespectful treatment
- Institutional distrust affecting long-term health outcomes
Clinical outcome implications:
Research-documented correlations:
- Higher complication rates in hospitals lacking bariatric-appropriate facilities
- Extended hospital stays necessitated by equipment inadequacy and complications
- Reduced patient satisfaction affecting institutional reputation and reimbursement
- Increased medication requirements potentially resulting from stress and poor outcomes
- Higher readmission rates when patients avoid follow-up care due to prior negative experiences
- Better surgical outcomes with appropriate bariatric operating room equipment

Caregiver Safety and Injury Prevention
Inadequate bariatric equipment directly increases caregiver injury risks affecting staff retention and institutional costs.
Caregiver injury patterns with bariatric patients:
Common injury types:
- Back and spinal injuries from improper lifting of patients using standard equipment
- Shoulder and rotator cuff damage from repeated strain during transfers
- Knee and lower extremity injuries from awkward positioning during patient assist
- Crush injuries when inadequate equipment fails during patient transfer
- Repetitive strain injuries from compensating for inadequate equipment
- Psychological injuries from guilt over patient harm or frustration with inadequate resources
Cost implications of inadequate equipment:
- Workers’ compensation claims averaging $5,000-$50,000+ per significant injury
- Lost productivity from staff absence and replacement
- Staff retention challenges affecting institutional stability
- Litigation costs from employee injury lawsuits
- Regulatory violations resulting in fines or license restrictions
- Training costs replacing injured or departing staff
Proper bariatric equipment reducing injury risk:
Protective mechanisms:
- Powered lifting systems eliminating manual lifting strain
- Appropriate equipment weight distribution enabling safe patient handling
- Staff training protocols emphasizing safe transfer techniques
- Adequate staffing levels preventing overwork and fatigue-related errors
- Ergonomic assessment identifying risks and implementing controls
- Regular maintenance preventing equipment failure during critical moments
Institutional Liability and Compliance
Inadequate bariatric furniture creates significant institutional liability affecting insurance, accreditation, and legal exposure.
Liability exposure factors:
Legal and compliance considerations:
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requiring appropriate accommodation for disabled patients
- Joint Commission standards increasingly requiring bariatric accommodation
- CMS and payer expectations regarding inclusive facility design
- State and local regulations potentially mandating bariatric equipment
- Informed consent implications when patients cannot safely access care
- Negligence liability when facility failure results in patient harm
Insurance and financial implications:
- Premium increases reflecting elevated risk profile
- Coverage denials for incidents involving equipment inadequacy
- Self-insurance exposure if catastrophic injury occurs
- Litigation costs defending against patient or employee claims
- Operational costs of equipment failure or replacement during patient care
- Revenue implications of regulatory penalties or reimbursement restrictions
| Table 4: Safety and Liability Considerations for Bariatric Facilities |
| Safety Factor | Risk Without Bariatric Equipment | Protection With Bariatric Equipment | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Fall Risk | High risk of injury/mortality | Appropriate, safe surfaces | ADA compliance, patient safety |
| Caregiver Injury | High back/strain injury risk | Reduced injury through powered assists | Workers’ compensation, duty of care |
| Equipment Failure | Catastrophic injury risk | Rated for patient weight safely | Liability prevention, patient protection |
| Dignified Care | Humiliation, healthcare avoidance | Respectful, appropriate accommodation | Ethical care, patient equity |
| Regulatory Compliance | Potential violations and fines | Standard-compliant facility | JC standards, state regulations |
Procurement, Selection, and Implementation Strategies
Facility Assessment and Equipment Needs Planning
Effective bariatric furniture implementation requires systematic assessment of patient populations and institutional needs.
Population analysis and planning:
Data-driven assessment:
- Current patient demographics including weight and BMI distributions
- Projected population trends anticipating future patient population characteristics
- Specific departmental needs (ED, ICU, surgical, etc.) requiring bariatric equipment
- High-volume vs. specialty areas determining equipment distribution
- ADA accommodation requirements ensuring legal compliance
- Budget constraints and phasing enabling realistic implementation
Equipment distribution planning:
Strategic placement considerations:
- All patient rooms requiring at least standard-capacity equipment for patient safety
- 50-75% bariatric capacity in facilities serving high-volume bariatric populations
- Selected super-bariatric equipment for exceptional cases or specialized programs
- Examination and procedure areas requiring appropriate equipment for diagnostic accuracy
- Bathroom facilities universally modified for bariatric access and safety
- Transfer and mobility equipment in all patient care areas
Vendor and Product Selection:
Key selection criteria:
Equipment specifications:
- Weight capacity ratings meeting or exceeding patient population needs
- Documented safety testing and regulatory compliance (FDA, manufacturer certifications)
- Durability and reliability for intensive use in healthcare settings
- Service and support infrastructure ensuring maintenance and repair capability
- Parts availability supporting long-term functionality
- Warranty coverage protecting institutional investment
Vendor evaluation:
- Experience with healthcare facilities and bariatric specialization
- References and case studies from comparable institutions
- Financial stability ensuring long-term business viability
- Training and support services for staff education and troubleshooting
- Responsiveness to equipment issues affecting patient safety
- Competitive pricing within institutional budget parameters
Implementation and Staff Training
Successful bariatric furniture implementation requires comprehensive staff preparation and training.
Staff education and competency:
Training components:
- Safe patient handling techniques adapted for bariatric populations
- Equipment operation and safety protocols specific to installed equipment
- Maintenance and troubleshooting identifying problems before patient safety impact
- Dignity-centered care addressing attitudes and stigma toward bariatric patients
- Emergency procedures responding rapidly to equipment failure or patient emergency
- Regular refresher training maintaining competency and safety culture
Operational protocols:
Integration into care processes:
- Admission protocols assessing patient weight and communicating equipment needs
- Room assignment procedures placing bariatric patients in appropriately-equipped rooms
- Equipment inspection routines verifying functionality before patient use
- Maintenance schedules preventing equipment failure through preventive care
- Emergency response procedures addressing equipment failure or patient safety concerns
- Feedback mechanisms enabling staff to report inadequacy or concerns
Conclusion
Bariatric hospital furniture represents a critical equity and safety investment ensuring that healthcare facilities appropriately serve patients across all body sizes. Proper bariatric specifications directly impact patient outcomes, caregiver safety, institutional liability, and organizational values regarding inclusive, dignified care. Strategic furniture selection, appropriate capacity ratings, comprehensive staff training, and consistent maintenance create institutional infrastructure supporting safe, respectful care for bariatric populations.
Key implementation recommendations:
- Conduct comprehensive population assessment determining appropriate bariatric equipment distribution
- Select equipment meeting or exceeding anticipated patient weight ranges with adequate safety margins
- Implement facility-wide standards ensuring consistent availability of appropriately-sized equipment
- Train all staff on safe handling, equipment operation, and dignity-centered care principles
- Establish maintenance protocols ensuring reliable, safe equipment operation
- Monitor outcomes and gather feedback identifying gaps and refining implementation
Future bariatric furniture design trends emphasize innovative materials and mechanisms enabling higher weight capacities with improved comfort, technology integration supporting patient safety monitoring, universal design principles accommodating diverse body types and abilities, and modular systems enabling flexible facility adaptation to changing population needs. Healthcare facilities that commit to comprehensive bariatric furniture and environmental design will improve patient outcomes, enhance staff safety, reduce institutional liability, and establish themselves as leaders in equitable, inclusive healthcare serving all patients with respect and clinical excellence regardless of body size.
FAQ
1. What weight capacity should bariatric hospital furniture have?
Standard bariatric furniture should support 450-600 pounds minimum, with super-bariatric options accommodating 600-900+ pounds for heavier patients. Safety standards recommend equipment rated at 150-200% of anticipated maximum patient weight. Facilities should assess their patient population demographics determining appropriate capacity distribution. Conservative approach suggests having some equipment capacity for exceptional cases beyond typical patient population. Verify manufacturer ratings and ensure documentation of capacity specifications for accountability and safety.
2. What specific modifications make furniture bariatric-rated?
Bariatric modifications include reinforced frames using heavy-gauge steel, wider bases for stability, strengthened attachment points, wider seating surfaces (20-24 inches vs. standard 17-18 inches), and enhanced mechanical systems. Structural engineering addresses weight distribution preventing tip-over or collapse. Electrical systems (for motorized equipment) are rated for maximum-capacity operation. Safety margins built into specifications exceed actual expected use preventing failure under normal conditions. Cosmetic dimensions like width and depth also increase for patient comfort and safety.
3. Are bariatric hospital beds required by law?
ADA and state regulations increasingly expect appropriate accommodation for patients with disabilities including obesity. Joint Commission standards recommend bariatric equipment availability. CMS documentation increasingly reflects bariatric patient accommodation expectations. Specific legal mandates vary by jurisdiction but trend toward requiring appropriate equipment. Ethical standards require dignified care and appropriate accommodation. Institutional liability increases when facilities fail to provide appropriately-sized equipment leading to patient harm. Best practice assumes bariatric equipment should be standard in all hospitals.
4. How much more expensive is bariatric furniture?
Bariatric furniture typically costs 20-40% more than standard-capacity equipment due to reinforced construction and engineering. Examples: bariatric bed ($3,000-5,000) vs. standard bed ($2,000-3,500); bariatric stretcher ($2,500-4,000) vs. standard ($1,500-2,500). Volume purchasing and institutional pricing may reduce margins. Long-term value exceeds cost through preventing equipment failure, patient injury, and caregiver injury. Institutional liability from inadequate equipment can exceed equipment cost many times over. Healthcare financing increasingly supports bariatric equipment as standard operational expense.
5. What should be included in bariatric equipment maintenance?
Regular inspection should verify structural integrity and mechanical function. Documented maintenance schedules with professional servicing address wear patterns from heavy use. Testing of safety features (brakes, locking mechanisms, electrical systems) ensures functionality. Parts replacement addressing wear from heavy use prevents catastrophic failure. Manufacturer recommendations should guide maintenance frequency and procedures. Staff reporting of issues enables rapid response preventing patient safety incidents. Documentation creates accountability and supports compliance demonstration.
6. How can hospitals phase in bariatric equipment given budget constraints?
Priority approach: Start with patient rooms requiring 100% bariatric capacity, then examination areas, then bathroom facilities. High-volume areas first serving most patients before lower-volume specialty areas. Start with bed and basic transfer equipment then expand to procedure tables and specialized items. Advocacy for capital budgeting highlighting liability and outcome benefits often secures funding. Lease vs. purchase options may spread costs across fiscal years. Grant funding through health organizations may support specific equipment. Bundle purchasing through group-purchasing organizations may reduce unit costs enabling broader coverage.
